Ray Optics
1. What is the distance between two convex lenses LA and LB with focal lengths FA and FB?
- FA+FB
- FA-FB
- FA
- FB
Answer: (a) FA+FB
2. If a medium has a critical angle for total internal reflection from the medium to vacuum as 300, what is the velocity of light in the medium?
- 0.5 × 108 m/s
- 3 × 108 m/s
- 1.5 × 108 m/s
- 0.2 × 108 m/s
Answer: (c) 1.5 × 108 m/s
3. The combination of which of the following processes results in the formation of a rainbow?
- Dispersion and Total Internal Reflection
- Dispersion and Absorption
- Refraction and Scattering
- Dispersion and Focussing
Answer: (a) Dispersion and Total Internal Reflection
4. What is the focal length of a double concave lens with a radius of curvature 20 cm, if the refractive index of the glass with respect to the air is 5/3?
- 20 cm
- -20 cm
- 15 cm
- -15 cm
Answer: (d) -15 cm
5. A diverging lens of power 65 D is combined with a convex lens of focal length, f = 20 cm. What are the power and focal length of the combination?
- 5 D, 33.7 cm
- 5 D, 66.7 cm
- 1.5 D, 33.7 cm
- -1.5 D, 66.7 cm
Answer: (b) 5 D, 66.7 cm
6. When a thin convex lens of glass 5D is immersed in a liquid, it behaves as a divergent lens of focal length 100 cm. What is the refractive index of the liquid?
- ⅓
- ⅔
- ⅗
- 5/3
Answer: (d) 5/3
7. The magnifying power of an astronomical telescope in normal adjustment is 100. What is the focal length of the objectives and eyepiece of the distance between them is 101 cm?
- 1 cm and 10 cm respectively
- 1 cm and 100 cm respectively
- 10 cm and 1 cm respectively
- 100 cm and 1 cm respectively
Answer: (d) 100 cm and 1 cm respectively
8. If an equiconvex lens of focal length f and power P is cut into half in thickness, what is the focal length and power of each half?
- Zero
- f/2
- f
- 2f
Answer: (d) 2f
9. A prism has an angle 600 and refractive index √2, what is the angle of minimum deviation?
- 900
- 600
- 450
- 300
Answer: (d) 300
10. What is the correct relationship between refractive indices n,n1 and n2 if the behaviour of light is as shown in the figure?

- n1>n
- n1<n
- n1=n
- None of the above
Answer: (b) n1<n
surface tension
Q1: When there are no external forces, the shape of a liquid drop is determined by
- Surface Tension of the liquid
- The density of the liquid
- The viscosity of the liquid
- The temperature of air only
Answer: (a) Surface Tension of the liquid
Q2: If T is the surface tension of the soap solution, the amount of work done in blowing a soap bubble from diameter D to a diameter 2D is
- 2πD2T
- 4πD2T
- 6πD2T
- 8πD2T
Answer: (c) 6πD2T
Q3: If the surface of a liquid is plane, then the angle of contact of the liquid with the walls of the container is
- Acute angle
- Obtuse angle
- 900
- 00
Answer: (d) 00
Q4: Raindrops are spherical in shape because of
- Capillary
- Surface Tension
- Downward motion
- Acceleration due to gravity
Answer: (b)Surface Tension
Q5: In a surface tension experiment with a capillary tube, the water rises up to 0.1m. If the same experiment is repeated on an artificial satellite which is revolving around the earth. The rise of water in a capillary tube is
- 0.1 m
- 9.8 m
- 0.98 m
- Full length of the capillary tube
Answer: (d) Full length of the capillary tube
Q6: At the critical temperature, the surface tension of the liquid
- Is zero
- Is infinity
- Is the same as that at the other temperature
- Cannot be determined
Answer: (a) Is zero
Q7: The surface of the water in contact with the glass wall is
- Plane
- Concave
- Convex
- Both a and b
Answer: (b) Concave
Q8: When a soap bubble is charged
- It contracts
- It expands
- It does not undergo any change in size
- None of these
Answer: (b) It expands
Q9: If common salt is dissolved in water, then the surface tension of saltwater is
- Increased
- Decreased
- Not changed
- First increases then decrease
Answer: (a) Increased
Q10: A drop of oil is placed on the surface of the water. Which of the following statements is correct?
- It will remain on it as a sphere
- It will spread as a thin layer
- It will partly be as spherical droplets and partly as thin films
- It will float at the distorted drop on the water surface.
Answer: (b) It will spread as a thin layer
ohms law
Q1: If a current of 5 Amperes flows through the conductor. The number of electrons per second will is
- 1.6 x 10-19
- 3.12 x 1019
- 4 x 1019
- 7.68 x 1020
Answer: (b) 3.12 x 1019
Q2: Ohm’s law is true for
- Metallic conductors at low temperature
- Metallic conductors at high temperature
- For electrolytes, when current passes through them
- For diode when current flows
Answer: (a) Metallic conductors at low temperature
Q3: An example of non-ohmic resistance is
- Diode
- Tungsten wire
- Carbon resistance
- Copper wire
Answer: (a) Diode
Q4: In a conductor, if 6-coulomb charge flows for 2 seconds. The value of electric current will be
- 3 ampere
- 3 volts
- 2 amperes
- 2 volts
Answer: 3 amperes
Q5: An EMF source of 8.0 V is connected to a purely resistive electrical appliance. An electric current of 2.0 A flows through it. What is the resistance offered by the electrical appliances?
- 4 ohm
- 6 ohm
- 2 ohm
- 3 ohm
Answer: (a) 4 ohm
Q6: A potential difference of 10 V is applied across a conductor whose resistance is 2.5 ohm. What is the value of current flowing through it?
- 4 amperes
- 2 amperes
- 6 amperes
- 10 amperes
Answer: (a) 4 amperes
Q7: If the conductor resistance is 50 ohm and the current passing through it is 5 A. What is the value of potential difference?
- 150 V
- 250 V
- 50 V
- 15 V
Answer: (b) 250 V
Q8: When the length of the conductor is doubled and the area of cross-section remains the same then its resistance
- Remains the same
- Will be doubled
- Will become half
- Will increase by four times
Answer: (b) Will be doubled
Q9: The current passing through a resistor in a circuit is 1 A when the voltage across the same resistor is 10 V. What is the value of current when the voltage across the resistor is 8 V
- 0.8 A
- 8 A
- 80 A
- 18 A
Answer: (a) 0.8 A
Q10: Two resistors R1 and R2 with resistance 5 ohms and 10 ohms respectively are connected in series. The voltage across R1 is 4 V. What will be the value of current across R2.
- 0.8 A
- 8 A
- 80 A
- 18 A
Answer: (a) 0.8 A
Ondielectrics
Q1: Which among the following is a dielectric?
- Copper
- Aluminium
- Plastic
- Ceramic
Answer: (d) Ceramic
Q2: How can a dielectric be converted to a conductor?
- Compression
- Heating
- Expanding
- Freezing
Answer:(b) Heating
Q3: Which of the following statements is true for a dielectric?
- Dielectrics are superconductors at high temperature
- Dielectrics are superconductors at low temperature
- The cannot become superconductors
- They have very less breakdown voltage
Answer:(b) Dielectrics are superconductors at low temperature
Q4: Dielectric materials do not have
- Free electrons
- Bound charge
- Proton
- neutron
Answer: (a) Free electrons
Q5: Dielectric materials are basically
- Insulators
- Semiconductors
- Superconductors
- conductors
Answer: (a) insulators
Q6: Find the dielectric constant for material with electric susceptibility of 5
- 4
- 6
- 7
- 3
Answer: (b) 6
Q7: When the air in a capacitor is replaced by a medium of dielectric constant K, the capacity
- Deceases K times
- Increases K times
- The K2 times
- Remains constant
Answer: (b) Increases K times
Q8: The dielectric constant cannot be
- Infinity
- 5
- 6
- 7
Answer: (a) Infinity
Q9: A capacitor of capacity C=10μF is connected to a constant voltage battery of 12 V. Now space between plates is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 5. The charge that flows now from the battery to the capacitor is
- 120 μC
- 699 μC
- 480 μC
- 24 μC
Answer: (c) 480 μC
Q10: The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is C. If a dielectric slab of thickness equal to one-fourth of the plate separation and dielectric constant K is inserted between the plates, then the capacitance becomes
- KC/2(K+1)
- 2KC/K+1
- 5KC/4K+1
- 4KC/3K+1
Answer: (d) 4KC/3K+1
Mirror formula based
Q1: A convex mirror of focal length f forms an image which is 1/n times the object. The distance of the object from the mirror is
- (n-1)f
- (n-1/n) f
- (n+1/n) f
- (n+1) f
Answer: (a) (n-1)f
Q2: Consider a concave mirror of focal length 50 cm. Where should the object be placed so that its image is twice the size of the object and inverted
- 60 cm
- 70 cm
- 75 cm
- 55 cm
Answer: (c) 75 cm
Q3: An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 16 cm from a concave mirror, which produces 3 cm high inverted image. What is the focal length of the mirror?
- -10 cm
- -9.6 cm
- 9.6 cm
- 8 cm
Answer: (b) -9.6 cm
Q4: An erect image 3 times the size of the object is obtained with a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. What is the position of the object?
- -12 cm
- 5 cm
- 10 cm
- -21 cm
Answer: (a) -12 cm
Q5: An object is placed at infinity in front of the convex mirror of radius of curvature 40 cm. How far is the image behind the mirror?
- 20 cm
- 25 cm
- 30 cm
- 35 cm
Answer: (a) 20 cm
Q6: The image formed by a convex mirror of focal length 30cm is a quarter of the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
- -90 cm
- 60 cm
- -75 cm
- -60 cm
Answer: (a) -90 cm
Q7: Convex mirror is used to form an image of the object. Which of the following statements is wrong?
- The image is erect
- The image is diminished in size
- The image is real
- The image lies between the pole and the focus
Answer: (c) The image is real
Q8: A lens having a focal distance of 30 cm is placed in front of an object, which is located at 1m from it. Where is an image of the object located?
- 40 cm
- 42.85 cm
- 52 cm
- 60 cm
Answer: (b) 42.85 cm
Q9: The focal length of a concave mirror is f and the distance from the object to the principle focus is x. The ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object is
- (f + x)/f
- f/x
- f2/x2
Answer: (b) f/x
Q10: In a concave mirror experiment, an object is placed at a distance x1 from the focus and the image is formed at a distance x2 from the focus. The focal length of the mirror would be
- x1x2
- (x1+x2)/2
- √x1x2
- √x1/x2
Answer: (c) √x1x2
Moving Coil Galvanometer
Q1: The deflection θ is related to the electric current I in a galvanometer by the relation
- I ∝ θ
- I ∝ tan θ
- I ∝ sin θ
- I ∝ cos θ
Answer: (a) I ∝ θ
Q2: A moving coil galvanometer carries a current I and the magnetic field B is radial. The coil has N number of turns and an effective area A. The torque acting on the coil of a moving coil galvanometer is given by
- NA2B2I
- NABI2
- NABI
- N2ABI
Answer: (c) NABI
Q3: The sensitivity of a moving coil galvanometer can be increased by decreasing
- The number of turns in the coil
- The area of the coil
- The magnetic field
- The couple per unit twist of the suspension
Answer: (d) The couple per unit twist of the suspension
Q4: In ballistic galvanometer, the frame on which the coil is wound is non-metallic. It is
- To avoid the production of induced e.m.f
- To avoid the production of eddy currents
- To increase the production of eddy currents
- To increase the production of induced e.m.f
Answer: (b) To avoid the production of eddy currents
Q5: The reason the coil is bound over the metallic frame in moving coil galvanometer is
- The metallic frame helps in oscillation
- The metallic frame helps in making steady deflection without any oscillation
- The metallic frame increases the magnetic field
- None of the above
Answer: (b) The metallic frame helps in making steady deflection without any oscillation
Q6: The deflection in moving coil galvanometer is
- Inversely proportional to the area of the coil
- Directly proportional to the torsional constant
- inversely proportional to the current flowing
- Directly proportional to the number of turns of the coil
Answer: (d) Directly proportional to the number of turns of the coil
Q7: The pole pieces of the magnet used in a pivoted coil galvanometer are
- Plane surfaces of a horse-shoe magnet
- Cylindrical surfaces of a bar magnet
- Plane surfaces of a bar magnet
- Cylindrical surfaces of a horse-shoe magnet
Answer: (d) Cylindrical surfaces of a horse-shoe magnet
Q8: A current-carrying rectangular coil placed in a uniform magnetic field. In which orientation will the coil rotate?
- In any orientation
- The magnetic field is parallel to the plane of the coil
- The magnetic field is at 450 with the plane of the coil
- The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane
Answer: (d) The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane
Q9: What is the shape of a magnet in moving coil galvanometer to make the radial magnetic field?
- Convex cylindrical magnet
- Horse-shoe magnet
- Concave cylindrical magnet
- None
Answer: (c) Concave cylindrical magnet
Q10: Phospher- bronze wire is used in suspension because it has
- A large couple per unit twist
- A small couple per unit twist
- Low conductivity
- High Sensitivity
Answer: (b) A small couple per unit twist
electric flux
Q1: If a unit positive charge is kept in the air. Then the total flux coming out of unit charge is
- 4πε0-1
- 4πε0
- ε0-1
- ε0
Answer: (c)ε0-1
Q2: What is the value of electric flux (Φ) on a plane of area 1m2 on which an electric field of 2 V/m crosses with an angle of 300.
- 1 Vm
- 2 Vm
- 3 Vm
- 4 Vm
Answer: (a) 1 Vm
Q3: Determine the electric flux of a flat square having an area of 10m2 is a uniform electric field of 8000 N/C passing perpendicular to it
- 8 x 105 Nm2/C
- 8 x 104 Nm2/C
- 16 x 105 Nm2/C
- 4 x 104 Nm2/C
Answer: (b) 8 x 104 Nm2/C
Q4: A plane surface is rotated in a uniform electric field. When is the flux of the electric field through the surface maximum?
- When the surface is perpendicular to the field
- When the surface is parallel to the field
- When the surface is at an angle of 300 with the field
- When the surface is at an angle of 450 with the field
Answer: (a) When the surface is perpendicular to the field
Q5: When is the flux through a surface taken as positive
- When the flux lines are directed inwards
- When the flux lines are directed outwards
- No flux lines through the surface
- Flux lines are parallel to each other
Answer: (b) When the flux lines are directed outwards
Q6: The net charge through a closed surface in a given medium depends on
- Size of the surface
- Charge of the surface
- The shape of the surface
- Area of the surface
Answer: (b) Charge of the surface
Q7: The dimension of electric flux is
- [M2L2T3A1]
- [MLT-3A-1]
- [M3L3T-3A-1]
- [ML3T -3A-1]
Answer: (d) [ML3T -3A-1]
Q8: The electric flux through a cubical Gaussian surface enclosing net charge q is q/ε0. While the electric flux through one face of a cube is
- q/ε0
- q/6ε0
- q/4πε0
- q/4ε0
Answer: (b) q/6ε0
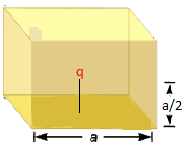
Q9: A point charge q is placed at a distance a/2 directly above the centre of the square of side a. The electric flux through the square is
- q/ε0
- q/6ε0
- q/4πε0
- q/4ε0
Answer: (b) q/6ε0
Explanation for Q9: Imagine a cube with charge q at the centre and the given square is one of its faces. So electric flux through the given square( one face) q/6ε0


.jpeg)
.png)

0 Comments